Gottard road tunnel, 2nd tube
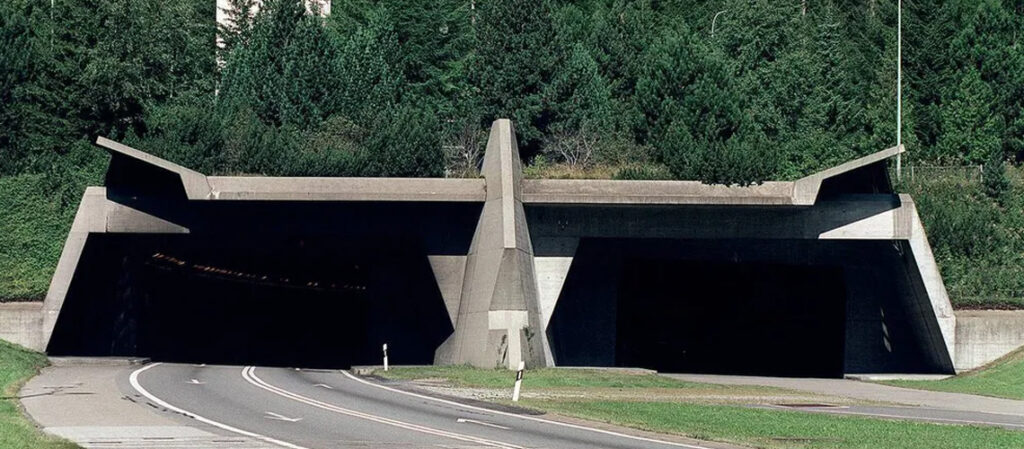

The first Gotthard road tunnel with a length of 17km has been in operation as a national road link between north Switzerland to the south, the canton of Ticino, since 1980. In order to ensure the functionality and safety of this important transport axis through the Alps, the first tube needs to be extensively repaired, […]
Konsko Dam
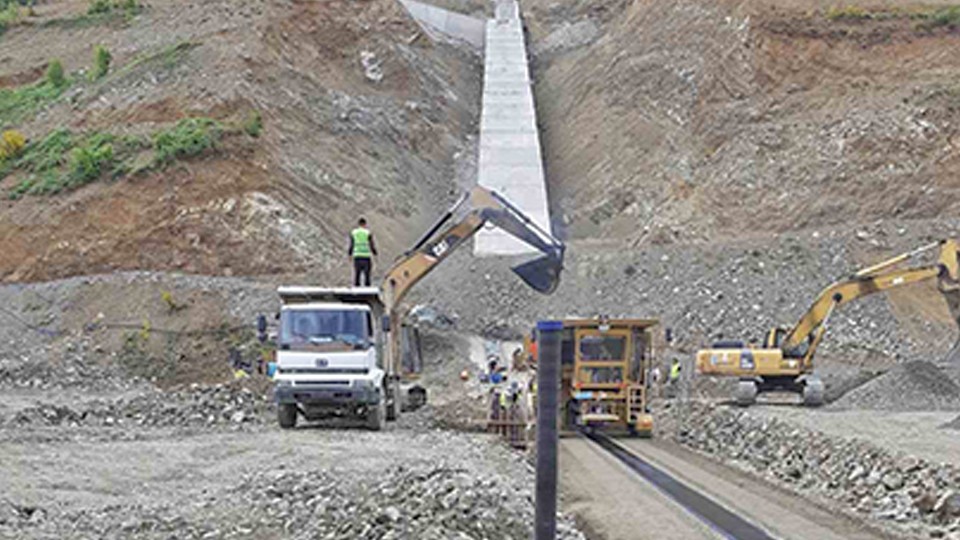

The dam is located close to the border between North Macedonia and Greece. It’s an embankment rock-fill dam with a central asphalt-concrete core as watertight element. The dam will be 80 m height, the cross section on top will be 340 m long, with a total embankment volume is approx. 1.4 m3 The main purpose […]
Grand Paris Express
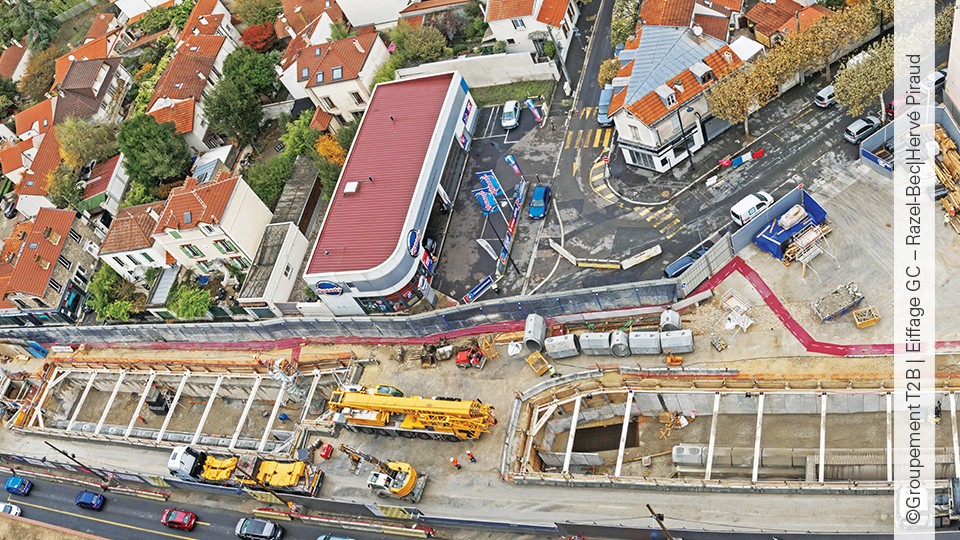

The Grand Paris Express is the largest urban project in Europe with the construction of 200 km of automatic lines, as much as the current metro, and 68 stations. The four new lines of the Grand Paris Express (15, 16, 17 and 18), as well as the line 14 extended to the north and south, […]
Urban Tunnelling: Hakata station of the Fukuoka city subway – Japan
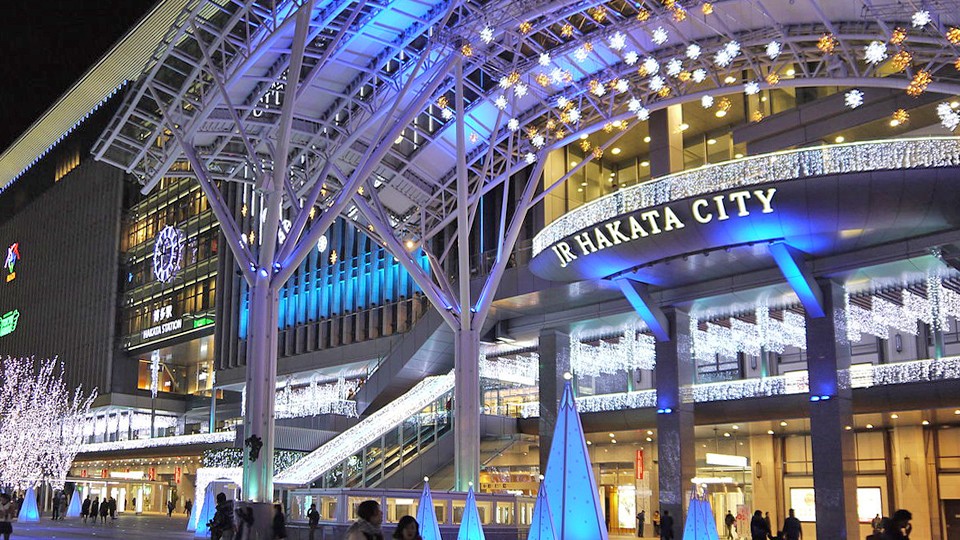

For the tunnel excavation of the Hakata station of the Fukuoka city subway in Japan partial excavation was carried out. A road with heavy traffic and different structures , as subground car park, gas pipelines, important sewers, are situated above the tunnel construction. Taking into account constraints as shallow overburden and unconsolidated ground above the […]
Inclinometri fissi BH-Profile
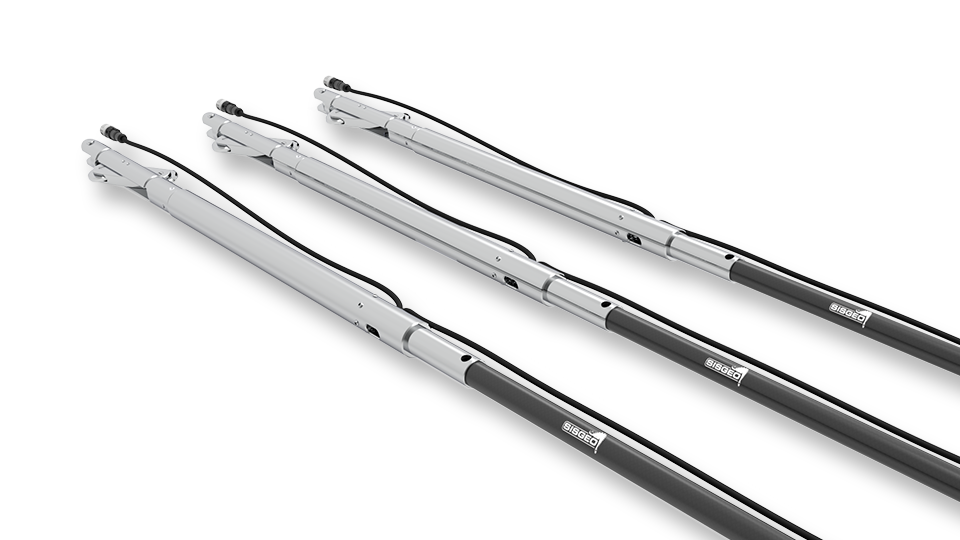
Codici di riferimento: S431HD, S432HD, S431HA, S432HA GLI INCLINOMETRI FISSI PER LA PROFILAZIONE DEL FORO (O BH-PROFILE) SONO STATI PROGETTATI PER IL MONITORAGGIO CONTINUO DI AREE INTERESSATE DA FENOMENI PARTICOLARMENTE CRITICI. Sono costituiti da un corpo tubolare in acciaio che alloggia il sensore inclinometrico MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical Systems), il carrello a bilancere, ed un’asta […]
Metropolitana di Roma – linea C
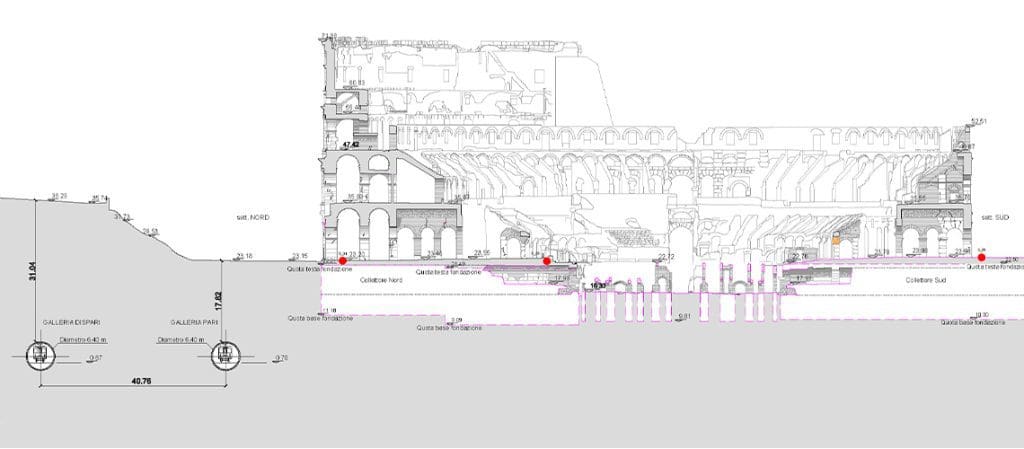
La linea C della metropolitana di Roma attraversa la città da nord-ovest (quartiere Della Vittoria) alla periferia est e si estende oltre il Grande Raccordo Anulare.La linea C ha un percorso completo di 25,6 km e 30 stazioni, passando per il centro storico.Il percorso sarà caratterizzato dal colore verde. Gli interscambi con le altre linee […]
Progetto Arosa Schafisgade – nuovo centro turistico – Svizzera
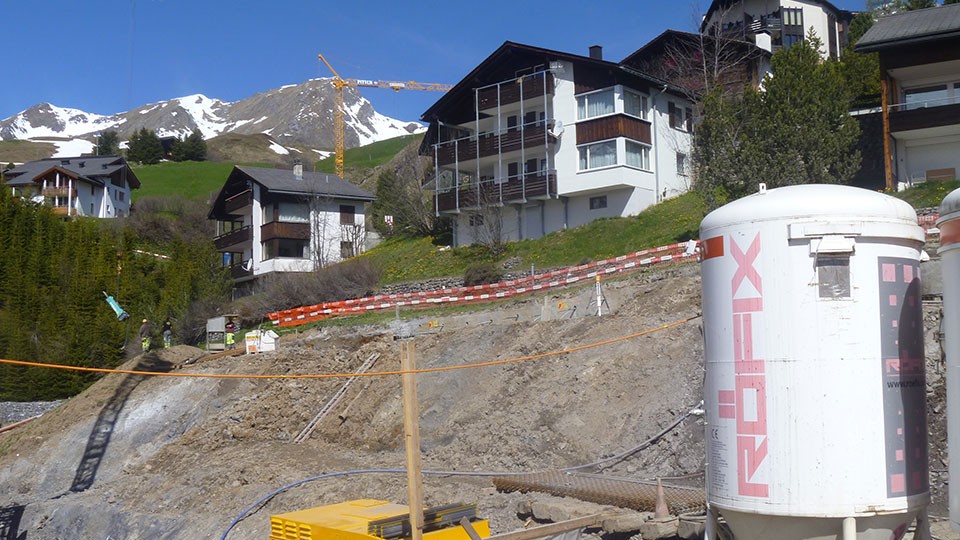

Il progetto Arosa Schafisgade prevede la costruzione di tre case con sei appartamenti di lusso ciascuna. Le case si trovano in un pendio potenzialmente instabile. Durante i lavori di scavo è stato necessario monitorare geodeticamente le case adiacenti a quelle di nuova costruzione. Tra il nuovo scavo e le case esistenti sono stati realizzati e […]
FAQ#116 – How do I configure a WR-Log digital node to read RS485 Sisgeo TIMED sensors?
Sisgeo digital instruments can operate in two powering modes: TIMED or ALWAYS-ON (for more information see F.A.Q.#094).A string of mixed instruments consisting of TIMED gauges and ALWAYS-ON gauges cannot work.The first thing to do is therefore to check that ALL connected instruments in your array are set to TIMED mode.You can check the powering mode […]
FAQ#095 – How long does a chain of digital sensors take to be read?
It mainly depends from the powering mode of the gauges (refer to FAQ#094 for the description of the powering modes). AN EXAMPLE WILL BETTER CLARIFY THE ANSWER. In a batch of 240 gauges, unless otherwise requested by the Customer, the addresses are settled from #001 up to #240. In a borehole is installed a chain of 30 […]
FAQ#094 – Which are the available powering modes for SISGEO digital sensors?
All SISGEO digital gauges can be settled in two different powering mode: The STANDARD powering mode is ALWAYS ON, so unless otherwise requested by the Customer, the sensors are settled as default in ALWAYS ON.
FAQ#087 – Could the IPI, BH Profile and DEX probes have problems in frozen water?
Sisgeo suggest that frozen water within the inclinometer casings is to be avoided due to following reasons: – Ice within the casing will affect functionality of the systems by blocking the individual probes;– Mechanical damages can occur to the probes, but also to the inclinometer casing due to the expansion of frozen water In any […]
FAQ#076 – Perchè è necessario aggiungere una resistenza di terminazione sull’ultimo sensore digitalizzato di ogni catena RS-485?
Tutti i sensori digitalizzati SISGEO (IPI, Tilmetri, H-Level, RDS ) usano il protocollo di comunicazione seriale RS-485. Il protocollo RS-485 contempla una resistenza di terminazione. Il collegamento raccomandato per una catena è il “punto-punto” (multidropped) in modalità bus (linea). Collegamenti a “stella”, ad“anello” o multipli non sono raccomandati. I datalogger SISGEO sono già predisposti con […]








