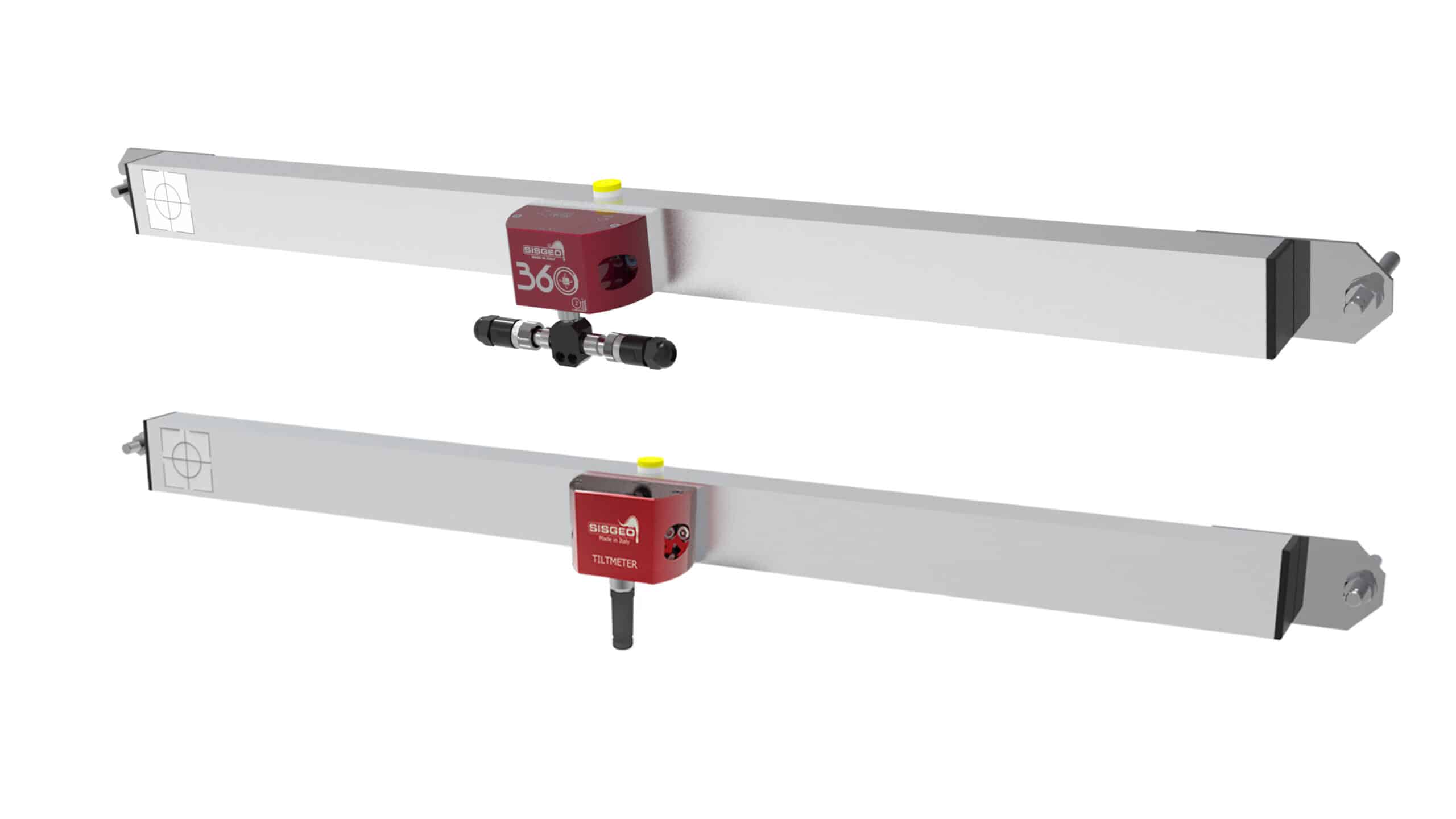
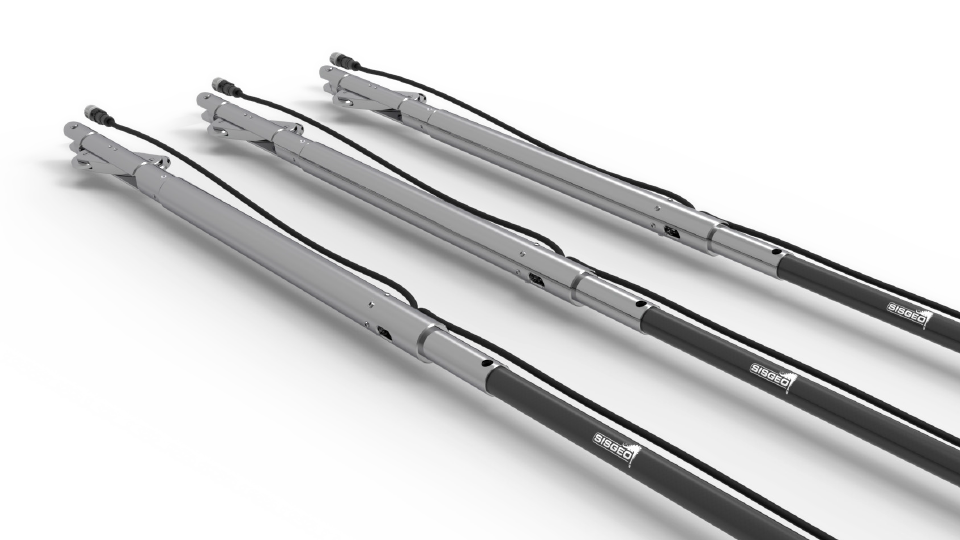
360° Chaine LT-Inclibus
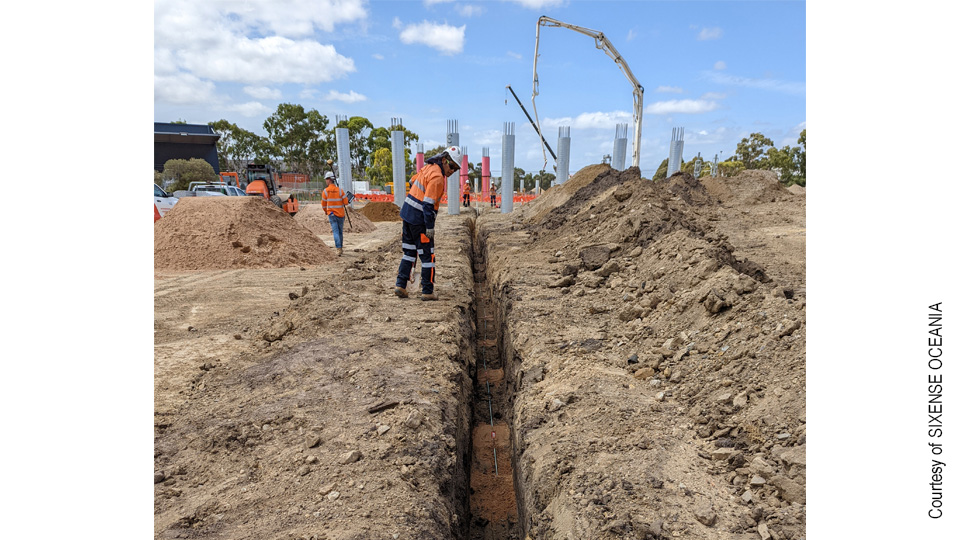
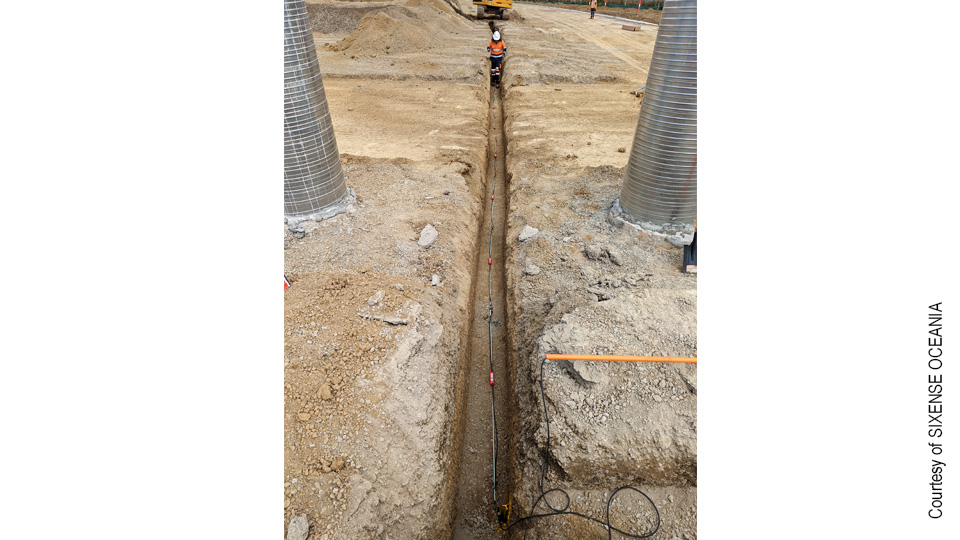
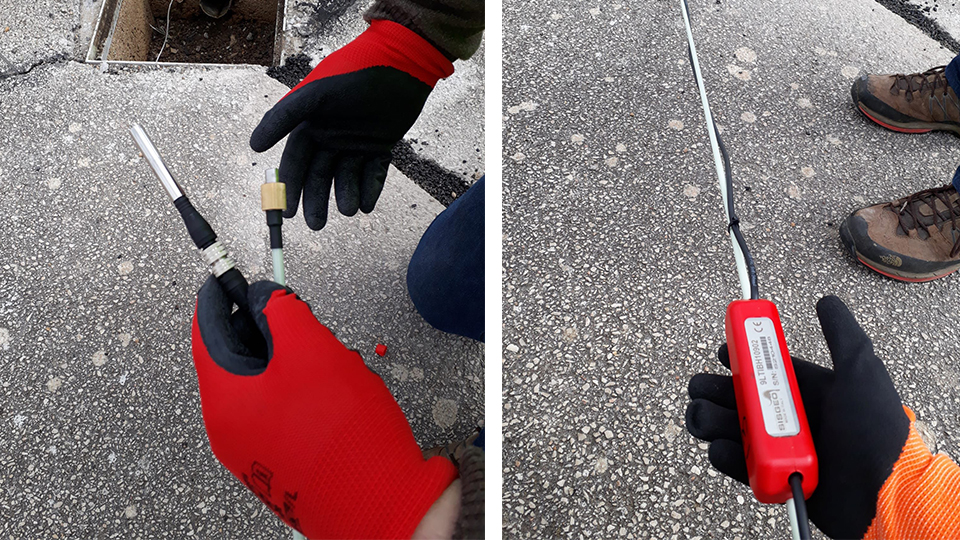
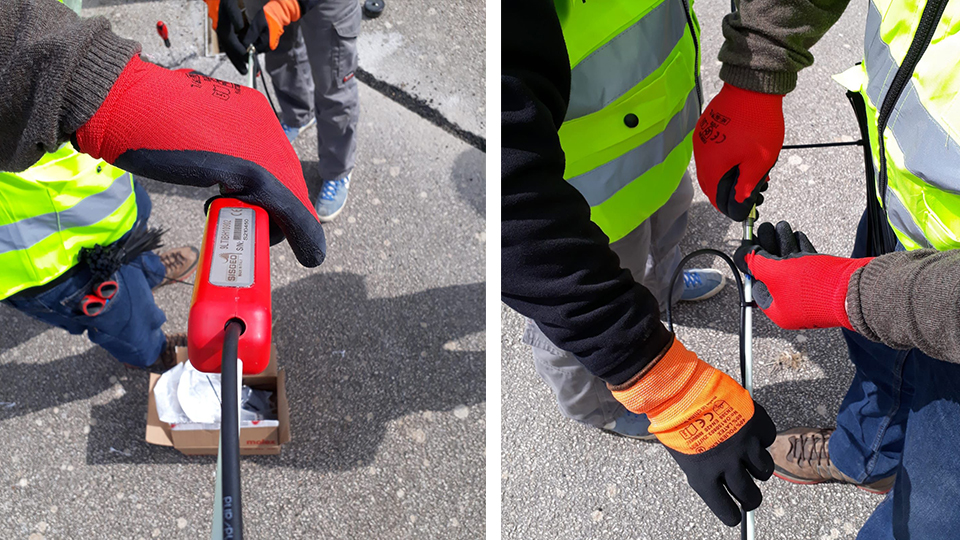
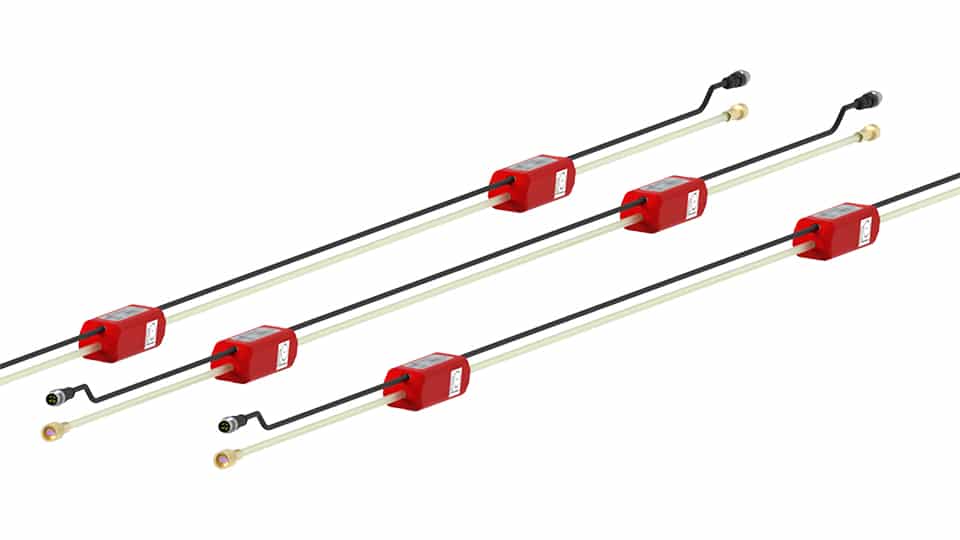






Codes de référence: LTIB
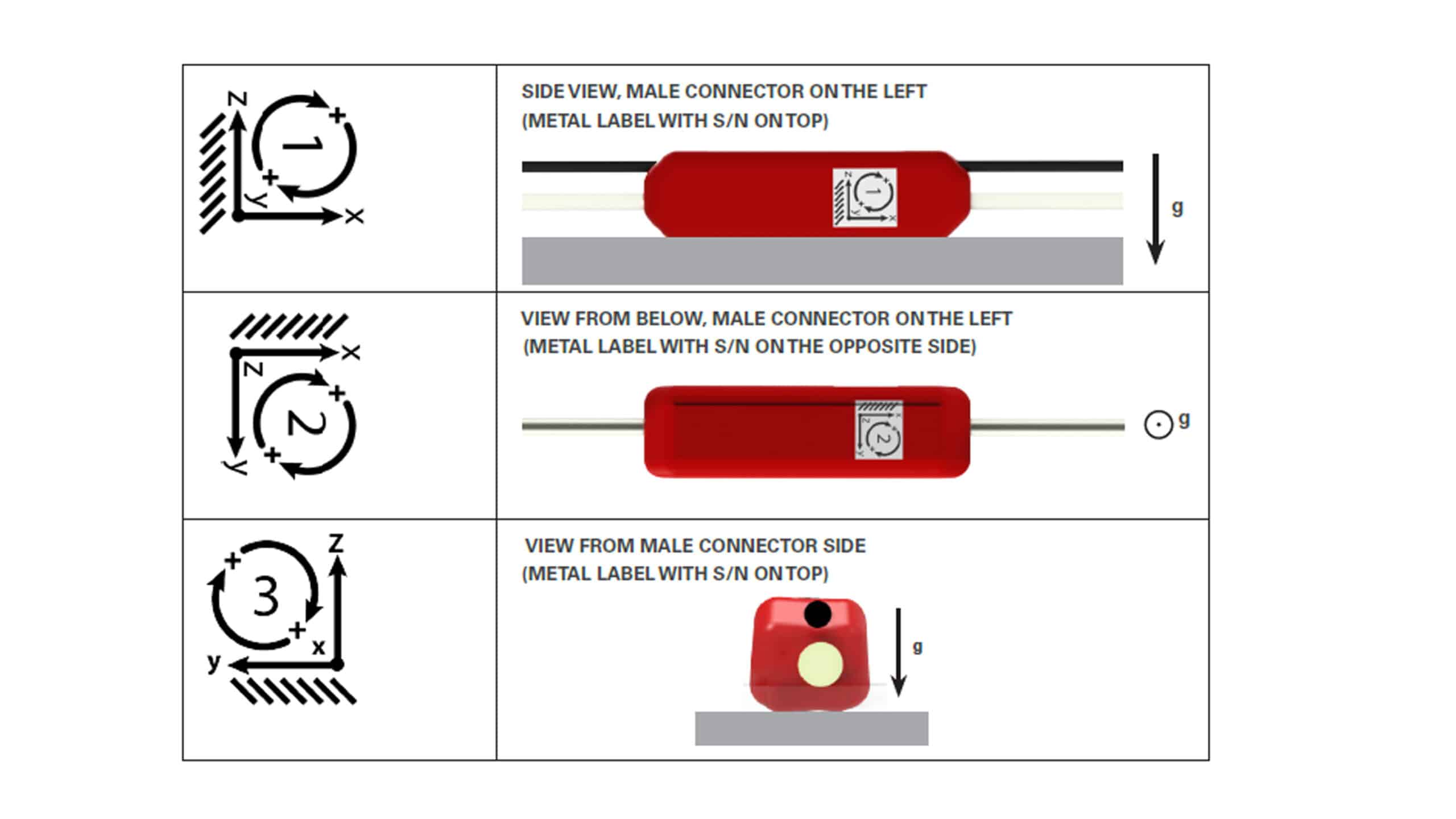
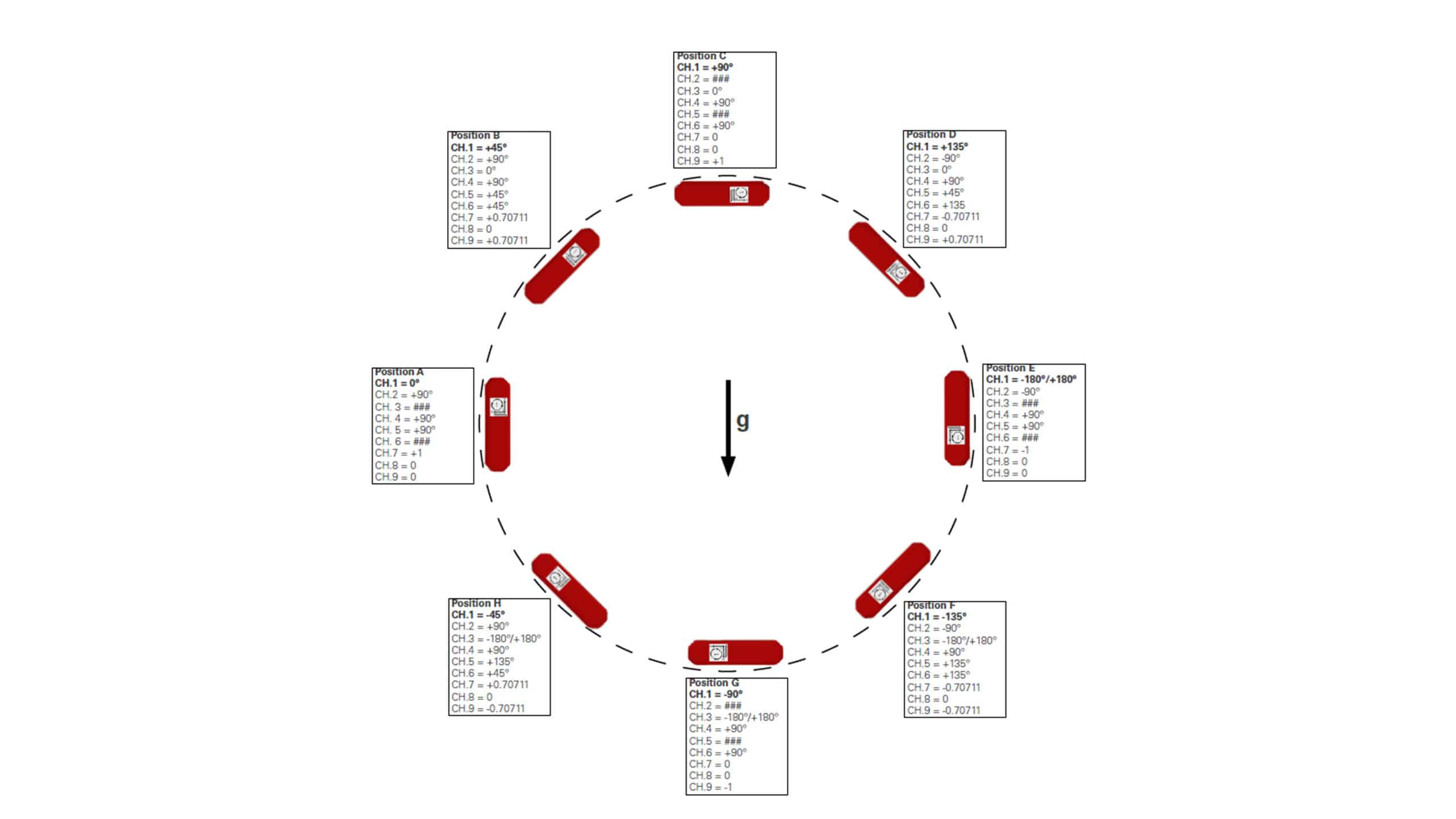
The principle of acceleration sensing is simple and reliable: inertia of a moving body is converted into force according to Newton’s second law. The basic elements of the accelerometer are the spring, the proof mass and the surrounding support structures. The spring connects the mass to the support.
When the speed of the sensor changes, the proof mass is forced to follow the change via the spring coupling. A force is needed to change the motion of the proof mass. Due to this force the spring is bent and the distance between the body and the proof mass changes in proportion to the acceleration.
Sisgeo’s MEMS inclinometers utilize capacitive sensor: in a capacitive sensor the support and the proof mass are insulated from each other, and their capacitance, or charge storage capacity, is measured. As the distance decreases, the capacitance increases and electric current travels towards the sensor; when the distance increases, the opposite occurs. The sensor converts the acceleration of the body into an electric signal.
The core of our MEMS inclinometers is a symmetrical, bulk-micromachined acceleration sensing element that has two sensing capacitors. Symmetry decreases temperature dependence and cross-axis sensitivity while improving linearity. All Sisgeo MEMS based instruments have a built-in NTC thermistor to measure also temperature value during readings.
Lisible par
Questions
sur ce
produit?
sur ce
produit?
Fiche technique
Manuel
Modbus
Faq connexes
Questions
sur ce
produit?
sur ce
produit?
Fiche technique
Manuel
Modbus
Faq connexes