What is tailings dams monitoring?
A tailings dam is a structure used in mining operations to store waste material, or tailings, that is produced during the processing of mineral ores. Tailings are the finely ground rock particles and other materials that are left over after the desired mineral has been extracted from the ore.
The design and construction of tailings dams are critical to ensure their stability and prevent environmental hazards such as dam failure, which can lead to catastrophic consequences such as flooding and pollution of waterways.
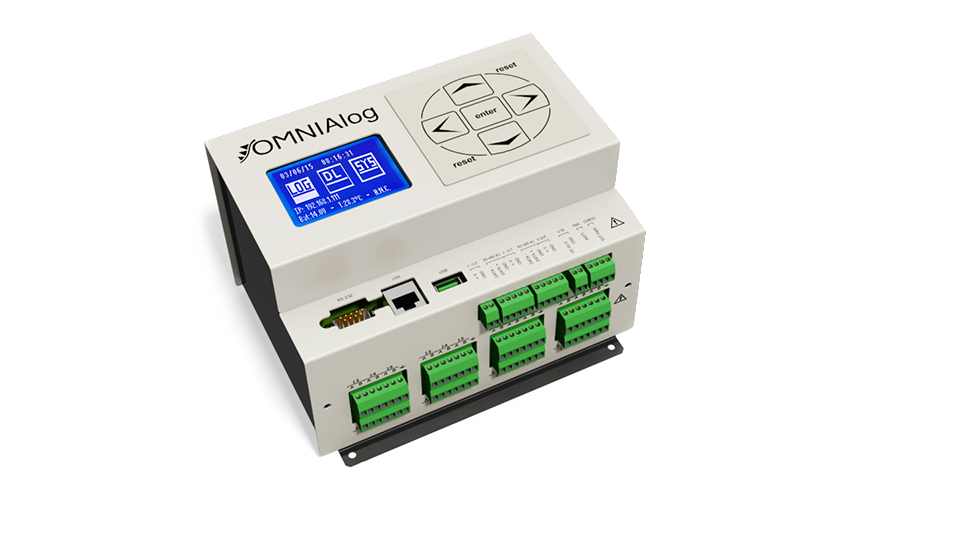
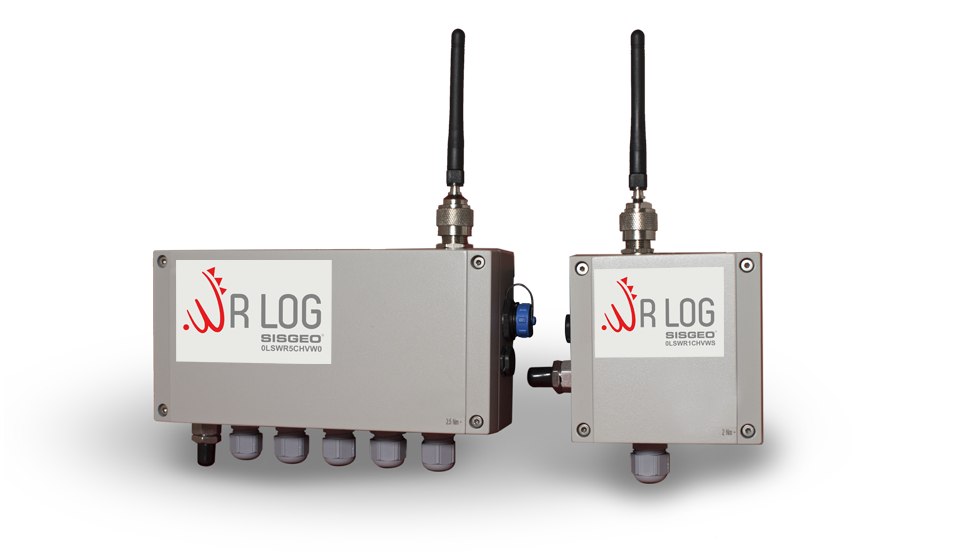
Geotechnical and hydrological monitoring are important aspects of tailings dam management to ensure the stability and safety of the dam and to prevent environmental damage.
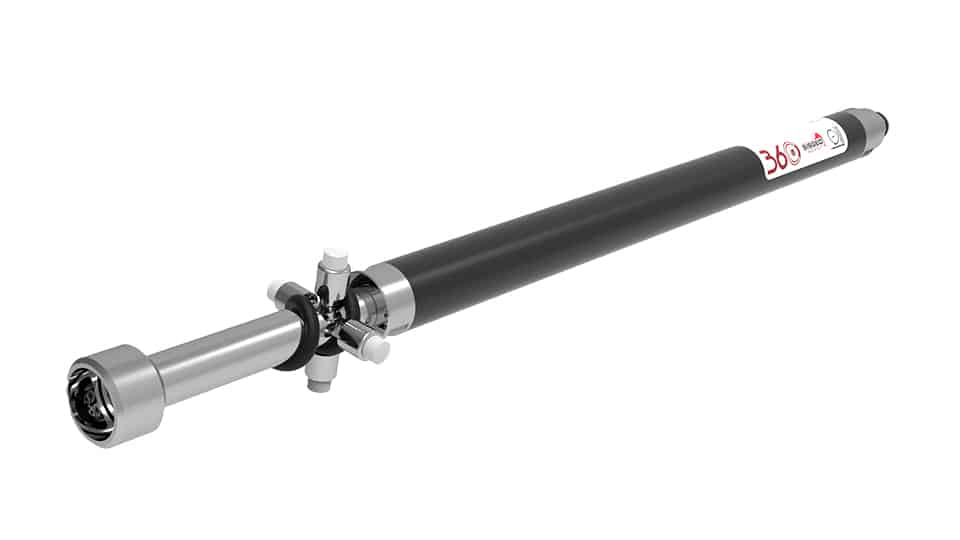
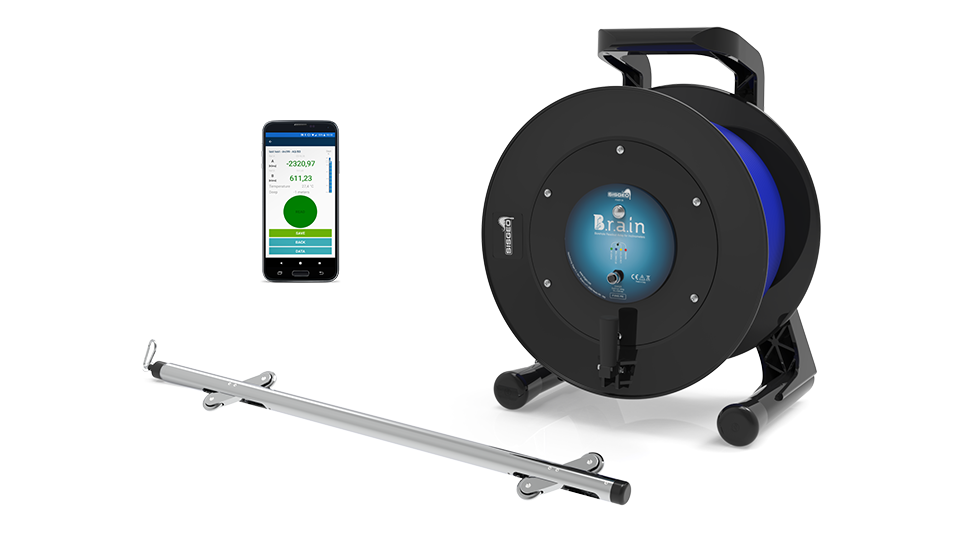
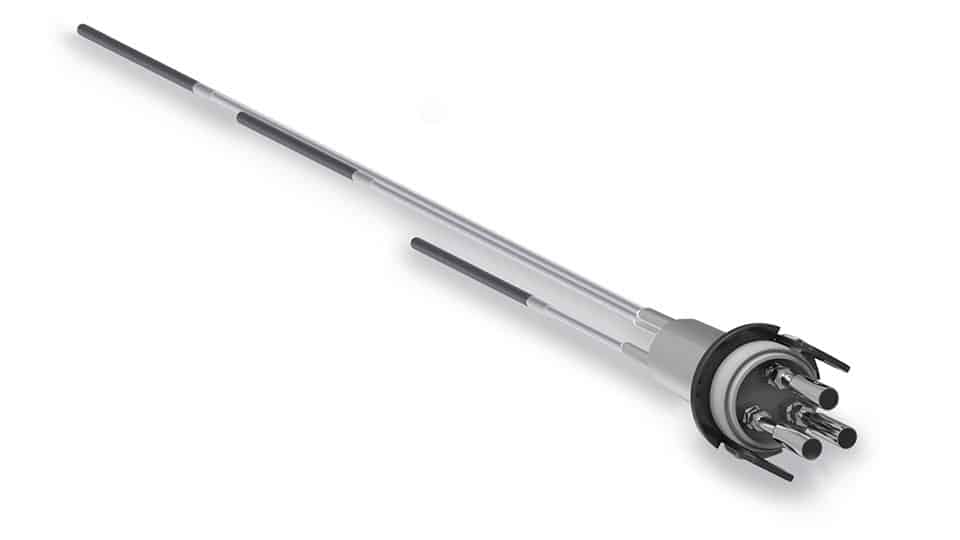
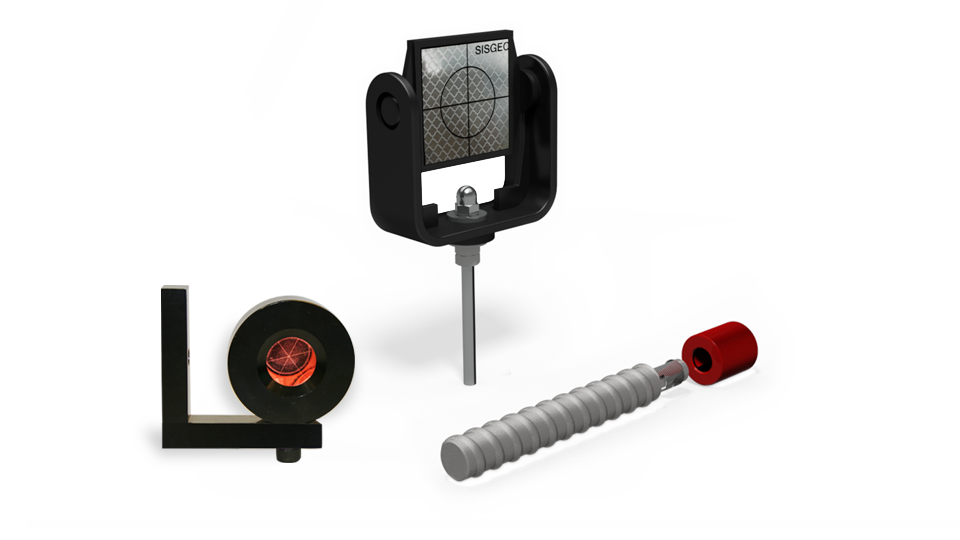
Geotechnical monitoring involves the use of instruments to verify the stability and behaviour of the dam, including its foundation, embankment, and slopes. This includes measuring parameters such as movement, settlement, and deformation of the dam and surrounding soil, as well as the presence of potential failure mechanisms such as cracks or fissures.
Hydrological monitoring involves the measurement of water levels and flow in the tailings dam and the surrounding environment. This includes monitoring the water levels in the tailings pond to prevent overflow or breaches, and monitoring water pressure under the pond.
The data collected from these monitoring activities can be used to assess the stability and safety of the tailings dam, to identify any potential risks or hazards, and to inform decision-making related to the operation and maintenance of the dam.